

sqlite> select Ename, Esalary from employee order by Eaddress ASC

In the below example order by clause is used which is ordering the records by Eaddress. You can use multiple columns with order by clause.

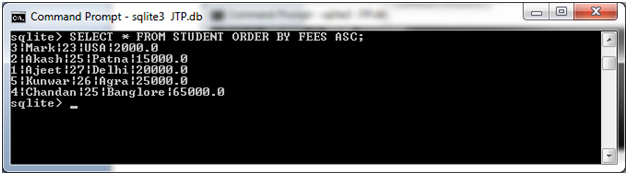
Order By Clause as the name symbolized it sorts the data is specified order i.e either ascending or descending. sqlite> select * from employee limit 2 offset 2 In the below query the limit clause will display 2 records as explained above and the offset will leave defined number of records in it. Using Offset with Limit clause will set a offset that after the defined offset the records will display. In the below example if you see the limit is set to “3”, then it will display first 3 records. In SQLite limit clause basically limits the output, it only display as much rows as defined in it, let’s see the example. Important Note:The basic difference between Like and Glob is that Glob is case-sensitive but like operator is not further Glob uses unix wildcards. sqlite> select Eno ,Ename from Employee where Ename glob 'R?v*' In following will return records as starting with ‘R’ followed by any letter after that ‘v’ than any number of letters. sqlite> select Esalary from Employee where ename glob '*t' In following example will return records with Ename ending with alphabet ‘t’. QuestionMark “?” – This represents single character. Asterisk “*” – This represents one or more characters. The wildcards are the special character which have some meaning for it. Glob clause is case_ sensitive unlike like clause. Glob clause is used to match text values against pattern using unix wildcards. sqlite> select Eno ,Ename from Employee where Ename like 'R_v%' sqlite> select Esalary from Employee where ename like '%t' Underscore “_” – This represents single character. Percentage “%” – This represents one or more characters. Like clause is used to match values using wildcards. Usage: sqlite> select Eno, Ename from Employee where Eaddress='Karnal' or Esalary=75000 Like we define a and, will be true if any of the condition either condition1, condition2 is true. With ‘OR’ clause we can define multiple conditions but it returns true if any specified conditions with it is true. Usage: sqlite> select Eno from Employee where Eaddress='Karnal'
AND Įxample: EMPLOYEE TABLE Eno Ename Esalary Eaddress Like we define a and, will be true if both are condition1, condition2 are true. With ‘AND’ clause we can define multiple conditions but it turns true if all specified conditions with it stands true. These clause is used to retrieve records or you can say multiple records with the specified condition define which these two clauses. Sqlite> select name from t1 where num=102 It is used with update, select, alter.etc. Where clause is used to filter out the result, for that define a condition with where clause.If the specified condition is true it return the records.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
